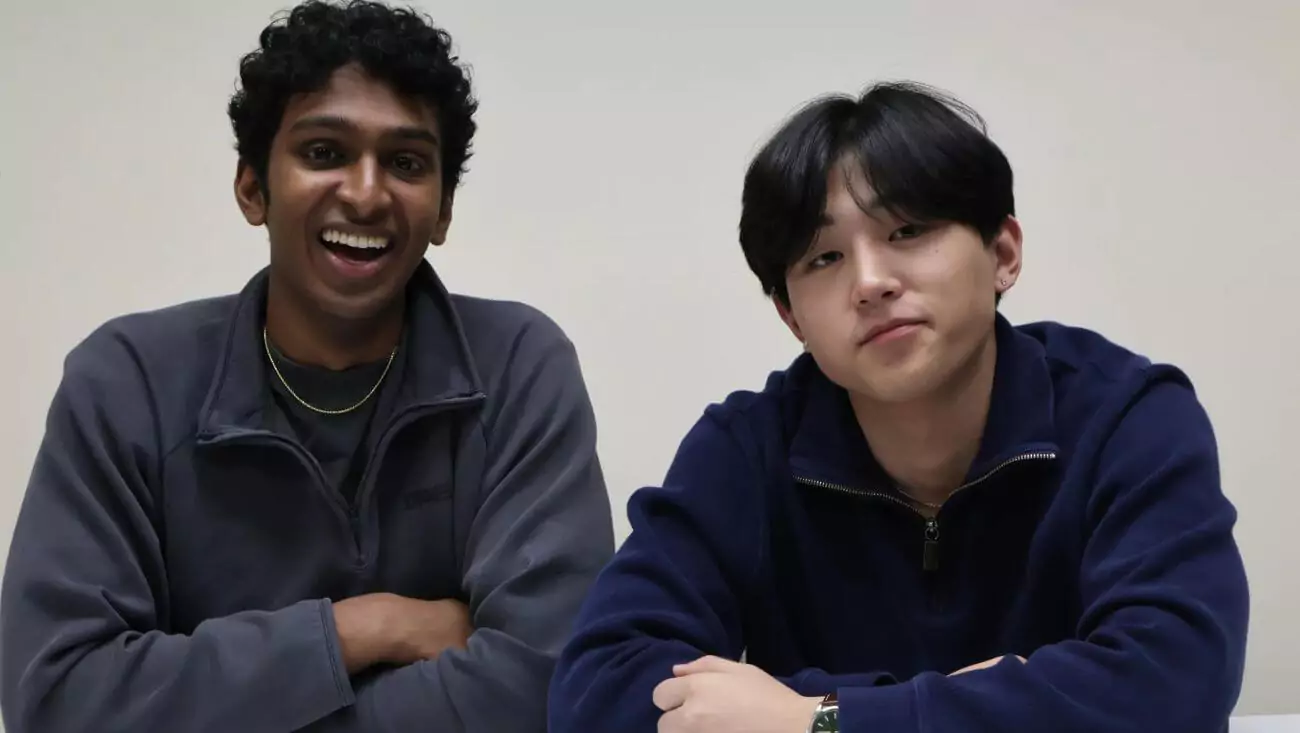
A 21-year-old entrepreneur who was suspended from Columbia University for creating an AI interview cheating tool has secured $5.3 million in seed funding for his startup. Jordan Chong, founder of the controversial AI company Cluely, is now expanding his technology despite significant concerns from educators about its implications for academic integrity.
“I got kicked out of Columbia for building an AI tool that helped me cheat on class interviews,” Chong candidly admitted in a statement reported by TechCrunch. Rather than abandoning his project after facing academic sanctions, the young entrepreneur refined his technology and successfully pitched it to investors.
Cluely is out. cheat on everything. pic.twitter.com/EsRXQaCfUI
— Roy (@im_roy_lee) April 20, 2025
The $5.3 million seed round was led by Founders Fund, with participation from several angel investors who see potential in Cluely’s approach to AI-assisted communication. This funding success is particularly noteworthy given the recent downturn in venture capital investment for AI startups.
“What began as a solution to my own academic challenges has evolved into something much bigger,” Chong explained during a recent press briefing. “We’re building tools that fundamentally change how people prepare for and handle high-pressure conversational situations.”
How Cluely’s Technology Works
According to Digital Watch, Cluely’s core technology analyzes patterns in interview questions and generates contextually appropriate responses based on a comprehensive database of successful answers. The system can provide real-time suggestions during interviews, helping users respond more effectively to unexpected questions.
The application initially focused on academic settings but has expanded to cover job interviews, professional assessments, and other high-stakes conversations. Users can access Cluely’s suggestions through mobile applications and browser extensions designed to operate discreetly during interview situations.
FirstPost reports that the company markets its product as an “AI communication assistant” rather than explicitly as a cheating tool, though critics argue the implications for academic and professional integrity are clear. The “cheat on everything” tagline has appeared in some of the company’s marketing materials, further fueling concerns about its intended use.
Educational Concerns and Ethics Debate
The success of Cluely has triggered intense debate among educators, employers, and ethics experts. Many express concern that such tools fundamentally undermine the purpose of assessments and interviews.
Dr. Sarah Martinez, an AI ethics researcher at Stanford University, commented, “Tools like Cluely raise fundamental questions about how we evaluate knowledge and skills. If someone can use AI to appear more competent than they actually are, what does that mean for our educational and professional systems?”
Columbia University, where Chong was previously enrolled, has strengthened its policies regarding AI-assisted academic work following the incident. The university now explicitly prohibits the use of AI tools during interviews and assessments without prior disclosure and approval.
Maeil Business Newspaper highlights that educational institutions worldwide are beginning to implement countermeasures against such technologies. These include more sophisticated monitoring systems and alternative assessment methods designed to be resistant to AI assistance.
The Growing Market for AI Communication Tools
Despite the controversies, market analysts predict significant growth in AI-assisted communication tools. The global market for such technologies is projected to reach $18 billion by 2028, according to recent industry reports.
Cluely is positioning itself at the forefront of this emerging sector. The company plans to use its newly secured funding to expand its team, enhance its core technology, and develop new features targeting various interview and assessment scenarios.
“We’re currently focused on interview preparation and assistance,” Chong stated, “but our vision extends to supporting all forms of high-stakes communication, from negotiation to public speaking and beyond.”
The company has already begun to explore partnerships with professional training programs that focus on communication skills, though many traditional educational institutions remain skeptical of the technology’s implications.
Evolving Regulatory Response
As AI communication tools like Cluely gain traction, they face an evolving regulatory landscape. Several states are considering legislation that would require disclosure when AI assistance is used in academic or professional settings.
“We anticipate increased regulatory attention as our technology becomes more widespread,” acknowledged Chong. “We’re committed to working with regulators to find the right balance between innovation and protecting the integrity of assessment systems.”
Legal experts suggest that the coming years will see significant development in how AI-assisted communication tools are regulated, particularly in educational and employment contexts. Some predict requirements for disclosure when such tools are used, while others anticipate technical countermeasures to detect AI assistance.
Digital Watch notes that regulatory bodies worldwide are still catching up to the implications of AI cheating tools, creating a window of opportunity for companies like Cluely to establish themselves before more comprehensive regulations are implemented.
Transformation of Assessment Methods
The rise of tools like Cluely is forcing educational institutions and employers to reconsider traditional assessment methods. Many are already shifting toward evaluation approaches that are more difficult to game with AI assistance.
“We’re seeing increased interest in project-based assessments, collaborative problem-solving exercises, and demonstrations of skills in controlled environments,” explained Dr. Jennifer Wise, an expert in educational assessment. “The goal is to evaluate capabilities in ways that AI can’t easily enhance.”
Some forward-thinking organizations have embraced AI as part of the assessment process, explicitly allowing candidates to use AI tools while focusing evaluation on how effectively they leverage these resources.
The Future of AI-Assisted Performance
Beyond the immediate context of interviews and assessments, Cluely represents a broader trend toward AI-augmented human performance. This trend raises fundamental questions about how we define and value human capabilities in an era of increasingly sophisticated AI assistance.
“When everyone has access to AI tools that can enhance their performance, the definition of ‘qualified’ changes,” noted technology ethicist Dr. Robert Kim. “We may need to focus less on memorized knowledge and more on the ability to effectively collaborate with AI systems.”
For Chong and Cluely, these philosophical questions take a back seat to the immediate business opportunity. With $5.3 million in fresh funding, the company is poised for rapid growth despite its controversial origins.
Cluely’s success represents a significant moment in the evolving relationship between artificial intelligence and human assessment. Whether viewed as a concerning development or an inevitable technological evolution, it signals a future where the boundaries between human and AI capabilities continue to blur.
As Cluely prepares to deploy its newly secured funding to expand its controversial offerings, educators, employers, and regulators will be watching closely to determine how to respond to this new challenge to traditional assessment methods.