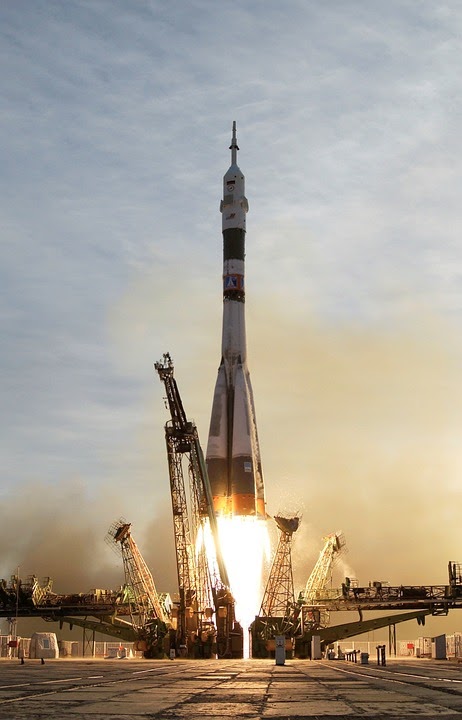
Space rockets have brought satellites & space stations into orbit and allowed people to reach space and the Moon. However, not many people know how rockets work and how these machines reach various places beyond the earth. From how they manage to escape the massive gravitation pulls to how they work without air in space, we will explain them all below.
Rocket Physics
Do you know that aside from fuel, a space rocket also brings oxygen supplies? It’s because a space rocket has an enormous engine that requires tons of oxygen to flame up fuel and propel it up into space. The size of the engine is incredibly huge, unlike ordinary jet planes flying in the air. Take a look at how rockets work in generating tons of forces to fight gravity, thrust, and move in empty space.
Forces
If there’s no air on the space, how can the rocket generate the force to move forward? Below the atmosphere, the jet engine pushes the air to lift the rocket upward by constantly firing the gas fuel downward, enormously. This rocket engine generates enormous forces that push your rocket to the sky. The rocket pushing force reacts to the gas force fired from the jet engine at equal levels. That’s how rockets work even against gravitational force and their overall weight.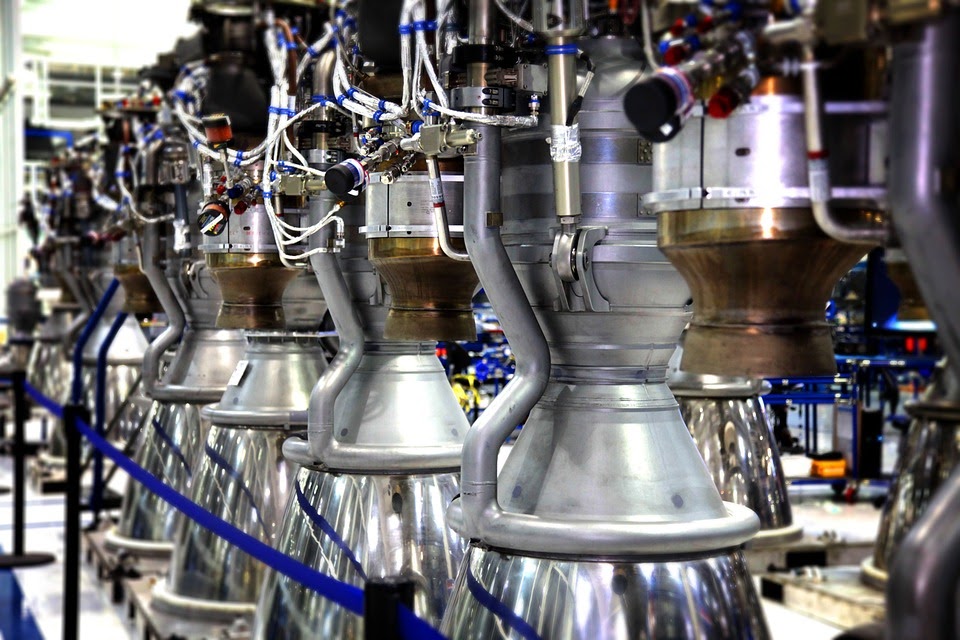
Thrust and drag
The jet engine of a rocket lifts the rocket straight into the sky without using wings, unlike jet planes. More specifically, the lifting force that pushes the rocket to the sky is called the ‘thrust’ and the one that pulls the rocket back is called ‘drag’. Once the rocket starts to take off, the air would soon resist the force and pull the rocket back or drag it downward, but with lesser force.
Escape velocity
The rocket jet creates enormous forces to overcome the gravity or the rocket’s weight. However, escaping the earth’s gravity would require more energy that is why the rocket constantly burns fuel to generate the escape velocity of 40,000 km/h at minimum. Only when the rocket has reached this level that it can curve up and escape the earth into space.
How do space rockets work without air?
Space has no air but space rockets can still move by shooting fuels from its engine. This action would drive an equal reaction that pushes the rocket forward into space. Newton’s law of motion explains how rockets work in empty space.
Key Parts of a Rocket
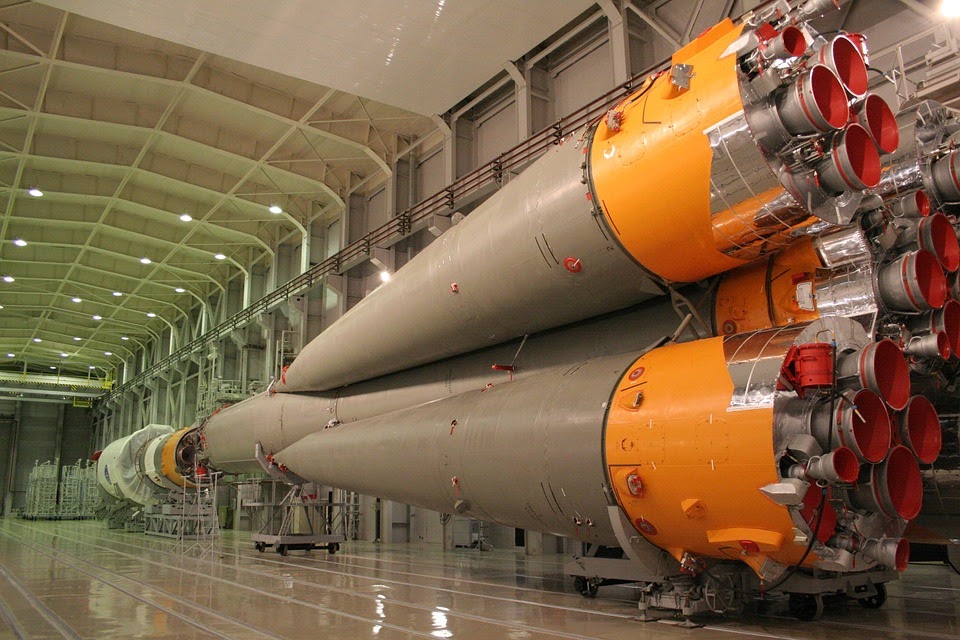 There are at least five key parts that build a rocket and these parts determine how they work properly. First, the rocket structure that works as the frame or fuselage where everything is installed. Second, a set of engines, fuel tanks, and boosters called the propulsion system. Third, the payload that contains suidance system containing a set of computerized controls and navigation. Fifth, there are also stages where today’s rockets put the parts into individual rockets.
There are at least five key parts that build a rocket and these parts determine how they work properly. First, the rocket structure that works as the frame or fuselage where everything is installed. Second, a set of engines, fuel tanks, and boosters called the propulsion system. Third, the payload that contains suidance system containing a set of computerized controls and navigation. Fifth, there are also stages where today’s rockets put the parts into individual rockets.
How Does a Rocket Engine Work
The propulsion system hosts the main engines that power the rocket upward. The liquid hydrogen and oxygen are pumped from the fuel tanks to the combustion chamber to power the engines. Most modern rockets have additional boosters that support and boost the main engines. However, these boosters are powered by solid fuels instead of liquid fuels.
Motion control for 10 engines
A rocket has particular motion control of 10 engines for how do rockets launch that consist of three stages. The first stage host the first nine engines taking a rocket to the top layer of the atmosphere through a curved trajectory with a two-axis motion control system hosting Gold, the SimplIQ, and the ExtrIQ servo drives that give around 10,000 W of power. Then, the pneumatic designed interstage removes the first stage along with the machines that separate it from Stage II. The second stage that hosts the fuel tank and the payload uses the 10th machine to reach the designated orbit.
https://www.elmomc.com/applications/drives-guide-space-missions/
How Rockets Work Video
For a better overview of youtube how rockets work to space, check the following videos.
Conclusion
As you’ve seen above, a rocket works differently from a jet plane as it carries its own oxygen to burn the fuels for power. It requires enormous energy to thrust the rocket into the orbit and against the drag of gravity forces. The motion of 10 engines manages and ensures the stages do their parts to reach the designated orbit successfully.